Water purification is an essential process in many industries. The Electrodeionization (EDI) or Continuous Electro Deionization (CEDI) process is one of the most efficient and cost-effective methods. CEDI is an ion exchange technology that uses electrical current to remove ions from water, resulting in high-purity water. This article will explore what is inside CEDI and how it works.
The components inside CEDI are:
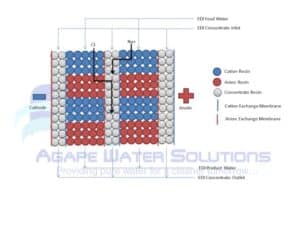
- Positively charged anode
- Negatively charged cathode
- Diluting chambers with mixed cation and anion resin (D-chambers)
- Concentrating chambers that remove the ions from the CEDI device (C-chambers)
- Cation Exchange membranes between Dilute and Concentrate chambers on the cathode side of dilute chambers.
- Anion Exchange membranes between Concentrate and Dilute chambers on anode side of dilute chambers.
What Is CEDI?
CEDI is an ion exchange water purification technology that uses ion exchange resin and membranes in a DC electrical current to remove ions from water. This impressive technology passes an electric current through a series of cell pairs which transports ions from the feed water to concentrate waste stream. This process results in high-purity water with low levels of dissolved solids, making it ideal for industrial applications such as semiconductor manufacturing and pharmaceutical production. Although original patents for this technology can be traced back to the early 50s, it was not until the mid 90’s that the technology advanced enough to provide consistent results.
How Does CEDI Work?
This highly technical process begins with a pre-treatment step such as reverse osmosis to remove suspended solids and bulk dissolved impurities from the feedwater.
The CEDI feed water enters the CEDI device and is split between multiple Dilute chambers. Water is purified as it passes the ion exchange resin and contaminants are trapped on the resin. The positively charged cations are attracted to the negatively charged cathode, migrate through the resin in the D-chamber until it reaches pass through cation exchange membrane into C-chambers. Likewise, the negatively charged anions are attracted to the positively charged anode, migrate through the resin in the D-chamber until it reaches pass through anion exchange membrane into C-chambers.
The contaminants are swept away into the concentrate stream, and exit the EDI device as a reject stream. The reject stream is still high quality, so the water can either be sent to local drain, or recovered to the pretreatment vented storage tank. Only about 5-10% of the feed water becomes concentrate reject in most cases.
Finally the DC electrical current splits water molecules H2O into hydrogen H+ and hydroxyl OH- ions. The hydrogen continuously regenerates the cation resin, and hydroxyls continuously regenerate anion resin. Note this is a continuous and chemical free process. So there is no acid or caustic regeneration necessary as with traditional mixed beds.
Advantages of CEDI
CEDI offers several advantages over traditional ion exchange processes, including:
- High efficiency: The CEDI process can achieve up to 99% removal efficiency for most ions, making it one of the most efficient methods of ion removal available today.
- Low operating costs: CEDI requires very little energy, resulting in lower operating costs for users.
- Low maintenance requirements: The membranes used in CEDI require minimal maintenance and can last up to 10 years or even longer with proper care and maintenance.
- Flexibility: The modular design of CEDI systems allows them to be easily scaled up or down depending on user needs. This makes them ideal for applications where flow rates may vary over time or where space is limited.
- Chemical free. No acid or sodium hydroxide is used to regenerate the resin, therefore no chemical regeneration systems, acid or caustic bulk storage, pH neutralization is necessary.
- Small footprints. CEDI systems have small space requirements and do not need all the ancillary equipment required with chemically regenerated systems.
CEDI is an efficient and cost-effective method for producing high-purity water with low levels of dissolved solids. It offers several advantages over traditional ion exchange processes, including high efficiency, low operating costs, low maintenance requirements, and flexibility in terms of scalability and space requirements. For these reasons, it has become increasingly popular among industrial users looking for reliable and cost-effective solutions for their water purification needs.
Suppose you’re looking for solutions for your industrial water purification needs. Or if you have questions about your current water purification solutions Agape Water Solutions is here to help. Our trained professionals can help with field audits, troubleshooting, and more. At Agape, we provide the best industrial water solutions.
Our trained personnel can check your plant’s specific operating conditions and requirements and recommend a proven solution. Our highly specialized process engineers can custom-design your system and select particular components and membranes to ensure the most reliable and consistent performance for years to come. We believe in excellence, and that’s the kind of products and services you’ll receive when you work with us. Contact us today to get started.
